Osteochondrosis is considered one of the most common diseases today, and it often affects women over the age of 25. The disease is characterized by an acute, rapid course, especially when comparing the course in male patients.
The pathological process accompanying the disease is the destruction of joint tissue and intervertebral disc. The pathology is the cause of headache in 30% of cases. If a woman experiences symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis, she should seek immediate medical help, which will help prevent further progression of the disease.

What is cervical osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a chronic disease that accompanies damage to one or more parts of the spine. Depending on this, the clinical presentation of the disease varies.
The main load falls on the lower back, but with the neck area failing, there are more problems. This is due to the anatomy of the body, with many fibers and nerve endings in the neck area, as well as blood vessels on which blood circulation in the brain depends.
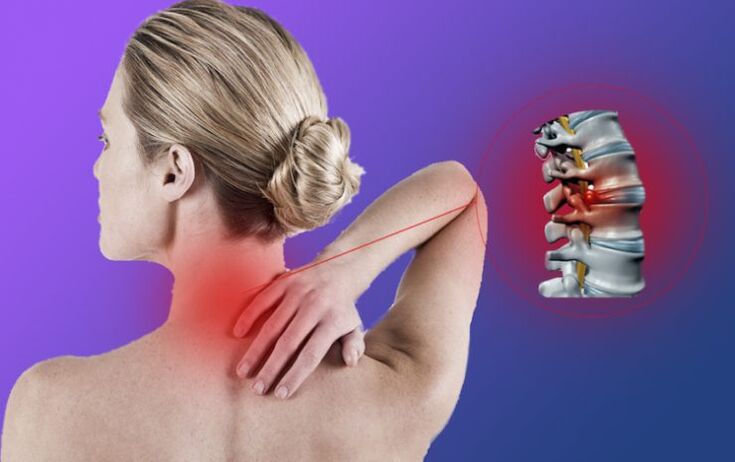
The cervical region is thought to be more vulnerable because of the proximity of the vertebrae and their proximity to the arteries involved in delivering nutrients to the brain. The displacement of the vertebrae results in compression of nerve roots and arteries, followed by changes in the intervertebral cartilage, hernias and protrusions. These changes in the intervertebral disc often have age-related features, and the disease can also manifest at a young age.
predisposing factors
There are many reasons for the occurrence of cervical osteochondrosis in women, and the predisposing factors include the following:
- taking hormonal drugs - this can lead to metabolic disturbances;
- increased load on the spine and spinal muscles (due to improper workplace organization, when working in hazardous industries or lifting weights, professional sports);
- Violation of eating habits, use of unhealthy food, lack of nutrition;
- Insufficient water intake (pure, free of harmful additives and impurities) - this can cause cartilage tissue, ligaments to dry out, causing toxins to clog the body;
- Low physical activity - against the background of lack of physical activity, impaired blood circulation to the muscles, insufficient nutrition of the intervertebral discs;
- Genetic predisposition, congenital curvature of the spine;
- Pre-existing disease (arthritis, arthropathy, neuralgia, vasospasm, etc. );
- Spinal metastatic injury;
- Continued stress - they are usually psychosomatic in nature, and against a background of tension, uncontrolled muscle contractions occur, with the result that the process of blood circulation, the flow of lymphatic fluid slows down, the deposition of toxins and toxins is observed.
Secondary risk factors:
- Incorrect spine position during sleep and rest, wrong choice of mattress and pillow;
- sleep without a pillow;
- Pregnant;
- overweight.
Age - As the body ages, vertebrae wear down, cartilage tissue wears down, calcium is washed away, weight is not distributed properly in the feet, and the spine is unevenly loaded.
Symptoms of cervical spondylosis in women
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine can be asymptomatic for long periods of time, many people attribute limited motor activity to fatigue, and pain is usually absent in the early stages of the disease.
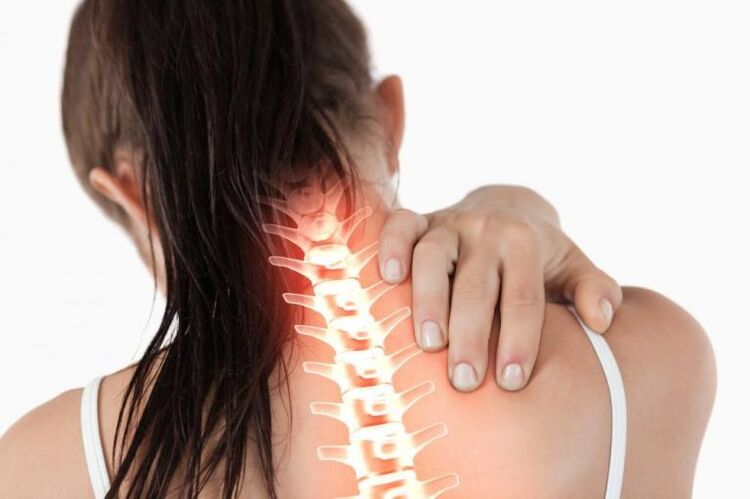
Pain is often associated with poor sleep and frequent stress. In some cases, signs of common cervical osteochondrosis in women can appear quickly. One day, a woman may feel fine, and the next day, the severe pain prevents her from moving freely or even lifting her head from her pillow. This condition is a reason to seek medical help, and at this stage you can easily cope with the signs of illness.
General symptoms of the disease
The symptoms of the acute phase of cervical osteochondrosis in women are more pronounced. Cartilage puts pressure on nerve roots and on arteries that run along the spine. There is a risk of short-term memory loss, and fainting often occurs due to lack of oxygen. Lack of treatment in the presence of pain, shoulder numbness, tingling fingers, and other symptoms can lead to paralysis.
reflex syndrome
The manifestations of cervical osteochondrosis in women are often associated with reflex syndrome, which occurs in the context of constant stimulation of receptors in the spinal cord, so that neurons are reflexively excited.
This leads to malnutrition, metabolic processes, and constriction of blood vessels and nerves.
Reflex syndromes are divided into:
- Pain - back pain, neck pain, pain in the back of the head, neck, shoulder/forearm at the same time.
- Muscle Supplements - Persistent muscle tension, leading to hypoxia, swelling, sealing.
Periodically, spasms may also occur in the muscles of the head, neck area, and shoulder girdle.
In the early stage of the disease, inferior oblique muscle syndrome, scapula-rib syndrome, vertebral artery syndrome, and scalene muscle tension often appear.
radiculopathy
Cervical vertebral osteochondrosis in women often develops radiculopathy with spinal cord nerve root vascular compression. Pathology is accompanied by impaired hand movement and loss of sensitivity. In this case, the function of the internal organs is also violated (pathology of urination, sexual dysfunction, hypertension, memory impairment). Invasion of blood vessels can occur unexpectedly, with sudden movements in the affected area.
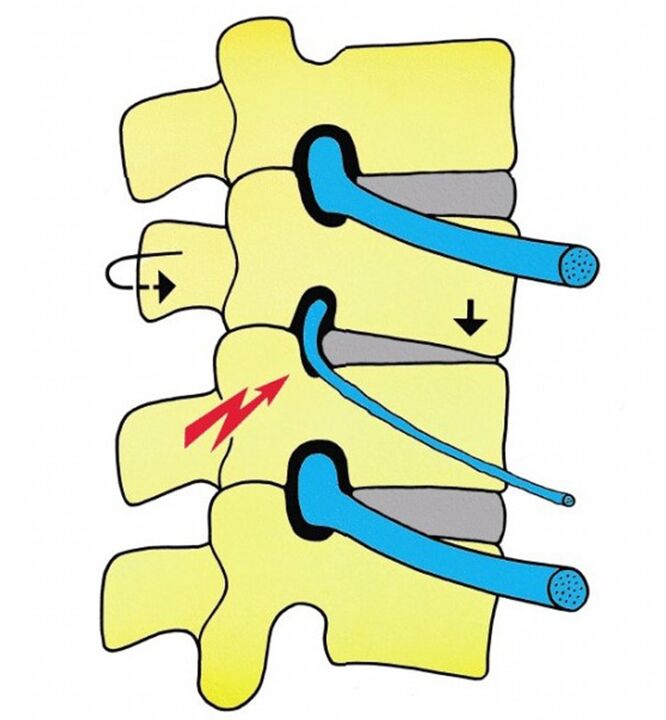
Vascular syndrome
In the context of symptoms of spinal cord vascular compression, women develop symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis and, in extreme cases, ischemic spinal stroke. This complication is accompanied by a violation of motor activities of the extremities, decreased sensitivity, and deterioration of the function of internal organs. Sometimes organs stop working, and if the kidneys fail, there is a high chance of death.
developmental stages of osteochondrosis
The disease has four stages, all accompanied by certain pathological changes.
Stage 1
In the first stage of disease development, damage to the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc is observed. This phenomenon occurs against the background of a violation of metabolic processes in the body, and due to dehydration, the core dries out, decreases in size and becomes less durable. The spine becomes more susceptible to physical stress and there are no pain syndromes at this stage. A diagnosis at this stage does not require medication.
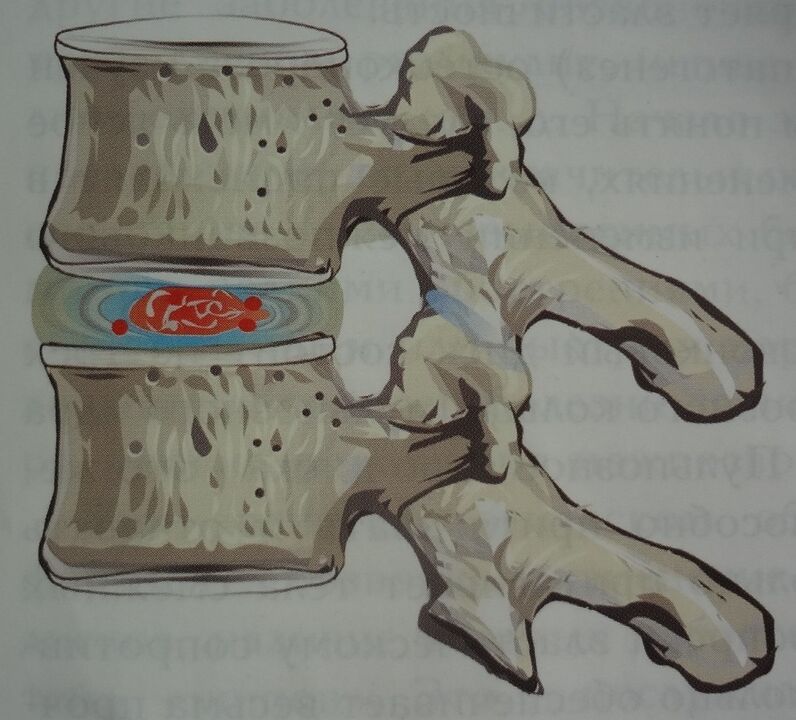
Stage 2
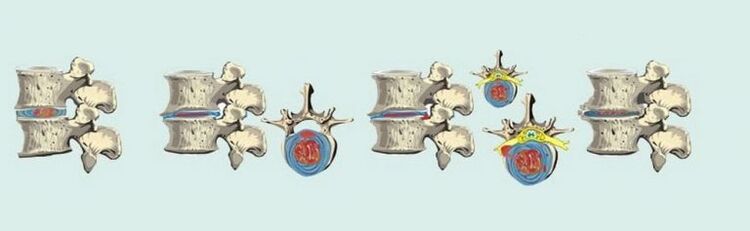
At this stage, due to the load on the spine, the annulus fibrosus is damaged, and tears and cracks appear on the surface of the disc. The rings became thinner and the core was transferred into tears and cracks, which caused them to expand. An enlarged disc herniation occurs outside the vertebrae, and the process is accompanied by pain.
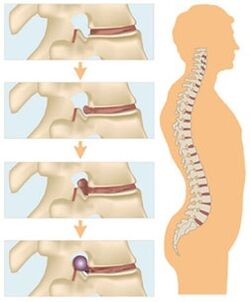
Stage 3
Third-degree osteochondrosis forms an intervertebral hernia with a tear in the annulus fibrosus. The nucleus pulposus moves into the subglottic space, causing a herniated disc. The pathological process results in damage to nearby blood vessels, muscle tissue, ligaments and nerves.
Stage 4
This phase is accompanied by degenerative recovery of the spine and lasts up to 12 months. During this time, the nature of bone growth changes, and they begin to widen, resulting in an increase in the area of the vertebrae. Thus, the formation of osteophytes occurs, as a result of which the mobility of the spine decreases and the destructive process stops.
treatment method
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis in women at any stage should primarily aim to eliminate the cause of the disease. Treatment should be comprehensive and this approach is beneficial to avoid further spread of the pathological process.
The effect of treatment should be aimed at restoring or activating lymphatic and venous outflow from the affected area. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is considered an excellent way to prevent and treat cervical osteochondrosis. Pain relievers are required as part of first aid, and NSAIDs are very effective.
After giving first aid, you should consult a doctor who will help prescribe the correct treatment.
medical
In the treatment of osteochondrosis, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (tablets, injections) - their action is aimed at reducing pain and eliminating inflammatory processes. Treatments can take several months, and they can negatively affect the function of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Steroid anti-inflammatory drugs (hormones) - used to treat severe pain. They have shown effectiveness in eliminating inflammation, pain, but also negatively affect the gastrointestinal tract.
- Antispasmodic - Effectively relieves muscle spasms, has a relaxing effect on muscles and activates the process of blood circulation.
- Epidural block - During the procedure, pain relievers and hormones are introduced into the space between the meninges and the periosteum of the vertebrae.
As part of osteochondrosis treatment, chondroprotective agents, muscle relaxants, are also required, and the dose and duration of treatment are prescribed by the doctor.
gymnastics
Physical therapy exercises for women with cervical osteochondrosis symptoms are recommended as directed by a doctor. All movements should be discussed with a specialist, as this can be exacerbated by incorrect positioning of the neck and arms.
Effective neck exercises:
- Lie down with your arms outstretched to your sides and your body slightly turned up. The right palm should be extended to the left and vice versa, repeat 5-6 times.
- Lie on your stomach, stretch your arms along your body, try to relax your muscles, and turn your head alternately in different directions. The edge of the ear should touch the floor, repeat 10 times.
- Stand straight with shoulders straight, slowly turn your head in different directions, and repeat 6-7 times.
- Bring your fingers together at the back of your head, bring your elbows together, and place your chin on your forearm and repeat 6-7 times.
All exercise is recommended on a regular basis, and only in this case the therapeutic effect can be achieved.
Physical Therapy and Massage
Pinching the vertebrae is accompanied by severe pain, and in order to eliminate the pathological manifestations of the disease, doctors prescribe physiotherapy. Their action is aimed at eliminating pain, reducing discomfort and activating circulatory processes.
For osteochondrosis, the following physical therapy methods are most commonly used:
- shock wave therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- acupuncture;
- Laser Treatment;
- balneotherapy;
- massage.
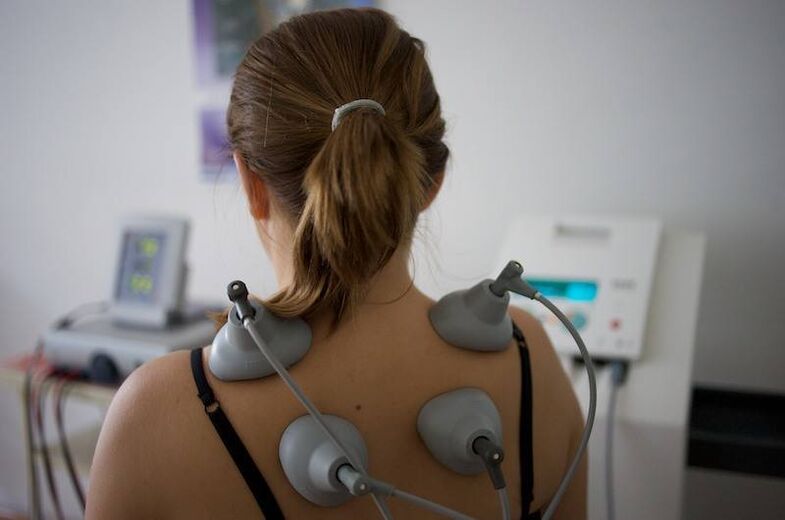
Massage has shown effectiveness in eliminating pain and, as a result, lost mobility is restored. The physical impact on the affected area activates the circulatory process, reduces tension and strengthens the muscles. The application of this method minimizes the risk of future pathological processes.
During treatment, different massage methods are used, depending to a large extent on the clinical situation, the physical characteristics of the patient, and the stage of the disease.
There are contraindications to massage, which must be taken into account before prescribing it. It should be noted that vascular lesions, hypertension, injury, and skin inflammation are also considered contraindications.
food
Diet plays an important role in osteochondrosis and must be balanced and it is best to contact a nutritionist. Salty food and mineral water intake should be minimized. It is recommended to eat less 5-6 times a day, fried, grilled, spicy should be replaced by steamed. It is recommended to prioritize protein products (beans, dairy products), chondroitin, sprouted grains, sesame seeds. Coffee, alcoholic beverages, strong tea are prohibited.

replacement therapy
Combining alternative treatments with traditional methods is also recommended. Need to consult a doctor first. This approach reduces the severity of symptoms, but does not eliminate the cause of the development of the pathological process. As part of folk remedies, ointments, infusions, decoctions, compresses, rubs, and baths are widely used. In their manufacture, various herbs, alcohol, oils, honey, etc. are used.
Valid recipes:
- Put a handful of chopped celery in 200ml of boiling water for 5 hours and drink 1 tablespoon of the filtered mixture. l. Everyday.
- Warm the green leaves of burdock or horseradish in a steam bath and apply to your neck for an hour.
- Mix honey and grated potatoes in equal proportions and use the mixture for compressing.

therapeutic bath
The role of the therapeutic bath:
- Heat - under the influence of elevated temperature, the process of blood circulation is accelerated, strengthened, the sensitivity of receptors increases, enzymes are activated, inflammatory processes are reduced;
- Mechanical - under water pressure, the blood circulation is activated, so the tissue is saturated with oxygen and useful elements;
- Chemical - After the addition of salts, minerals, plants, water, the healing properties are obtained, the bath also has a stimulating effect on the excretory system, as a result, the body's resistance to diseases increases.
The needles, salt, mustard bath is highly efficient and the process lasts 20-30 minutes. After the course of treatment, it is recommended to lie on a warm bed, as the cold will negate the full effect of the treatment. The procedure should be abandoned if there are cancer, heart and blood vessel problems.


















